Our article “How to choose your laser engraver” presents the many advantages of laser technology compared to other marking solutions. Let’s discover here the specificities of the different laser sources in order to choose a marking equipment adapted to your use. Each laser source has its own advantages and meets a specific need. Today we present the CO₂ laser, the fiber laser and the YAG laser which also includes the Green laser and the UV laser.
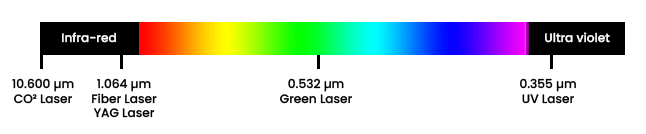
Laser marking is very popular in many industries. However, there are several types of laser sources for different uses and different materials to mark. What differentiates all these laser technologies is above all the wavelengths. They are positioned in the invisible spectrum of the ultraviolet and infra-red, or in the visible spectrum between the first two. Depending on their position on this graph, laser sources can (or cannot) mark certain materials.
Marking with fiber laser source for metal marking
The fiber laser is the most common laser marker on the market. Like the CO₂ laser, its wavelength is located in the infrared spectrum, but this one is at the limit of the visible spectrum (1.064 µm).
It is enormously used in the sectors of metallurgy, automotive, aeronautics and more generally in the mechanical industry. It is THE laser to choose for the realization of markings on all types of metals (steel, aluminum, titanium, carbide, alloys, etc…).
We offer a range of fiber laser marking Graphix.series (available in station use or integrated use) contact us to study your project together.

Why choose a fiber laser?
- It is an ultra-reliable laser source with a very high lifetime
- It can make very deep markings depending on the power of the laser
- The parameter setting enables easy adjustment of the marking result
- It requires very little maintenance
- Marking is carried out very quickly
- It is possible to carry out markings with relief or a discoloration on the part
Markings on organic materials using the CO₂ laser source.
The CO₂ laser source has the longest wavelength (10,600 µm). It is located in the invisible infrared spectrum. The specificity of this laser is that it works with electrically excited carbon dioxide. This gives it a fairly good performance but requires, however, more maintenance.
The CO₂ laser is ideal if you want to mark organic materials such as wood, plastic, glass, textile and cardboard. This laser technology burns and melts the material in contact with the surface to be marked thanks to the CO₂. Attention it is however one of the most energy consuming laser sources (up to 70kW).
What are the benefits of the CO2 laser?
- High marking speed
- Use on organic materials
- Can also cut certain materials
YAG laser markings or “crystal” laser, for sensitive materials
The YAG laser is ideal for marking plastics. Its wavelength is similar to that of the fiber laser (1.064 µm), however its structure is totally different. The YAG laser is powered by a neodymium doped diode, then the beam passes through different crystals. This laser structure allows it to perform markings on different materials, even the most sensitive and/or risky ones. In its “classic” configuration, the YAG laser is perfectly suited for marking metals and plastics.
The fact that crystals have been implanted in the YAG laser structure has made it possible to play with the wavelength of the laser source. Two new solutions were then developed:
The green laser designed for sensitive polymers
The Green laser is the only laser solution that positions its wavelength in the visible spectrum (532 µm). This short wavelength offers the possibility to mark many sensitive materials which are very often plastics and polymers. Other laser solutions have a lot of difficulties to mark flexible materials such as rubber for example because it is a very fragile material which reacts very badly to heat. It is important to know that the closer the wavelength is to the infrared, the more heat the laser generates. On the other hand, the laser will give off less heat if it is positioned near the ultraviolet.
Ultraviolet laser marking for cold marking
The UV laser source has the particularity of being the only laser marking technology in the invisible ultraviolet spectrum. It has the shortest wavelength used in the field of laser marking (0.355 µm) thanks to the use of additional crystals.
This laser source is used by companies who wish to carry out markings on rather sensitive parts. Indeed, the UV laser allows to carry out “cold” markings, which avoids any degradation of the part due to heat. It can be used, for example, for marking electronic components, solar panels, etc.
What are the advantages of choosing one of the YAG technologies? :
- Marking can be done cold which is ideal for heat sensitive parts
- Numerous wavelengths are available to accommodate different materials
Each need has its laser source
The choice of the source is an essential element for the realization of your future markings. The type of material you want to mark will have a significant impact on your laser selection, but also your usage. For example, maintenance requirements vary with each laser source, as do marking speed, marking depth, and life duration.
It is important to work with a specialist to help you choose your equipment, we are here to help you build your marking and traceability project!








