Marking types
Alphanumeric marking

Automatic alphanumeric marking

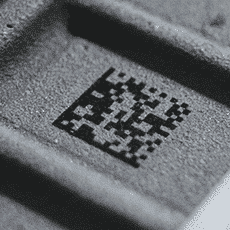
2D codes marking
Logo marking

Industrial marking is for many companies an important organizational and logistical system, a trusted means of communication and a method of protection and identification. Many needs are very common, but new applications and new types of marking are emerging regularly. Marking technologies have evolved quickly over time to meet a maximum of needs and to be able to carry out a multitude of types of marking.
It is now possible to make simple alphanumeric markings, perfect for repeating the same marking in series, but also variable alphanumeric markings such as serial numbers or time stamps. These markings are parameterized in advance by the operator so that the software automatically changes the characters of the marking as the operator wishes after each marking.
The marking of 2D codes such as Datamatrix or QR codes is more and more popular. This allows to register a maximum of information on a very small surface.
Finally, you can make logo markings, forms and pictograms to realize the “branding” of your products, to personalize them or to register manufacturing standards.
The locations of the different types of marking
Straight marking
Angular marking

Radiant marking

Mirror marking

Marking on cylinder

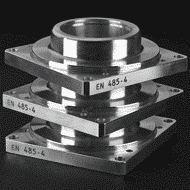
Multi-level marking

The location of the marking is an important element to consider when choosing your marking equipment and designing your marking files. In order to simplify the use of these markings ( readability, scanning of 2D codes, …) it is essential to choose the best marking zone and the right way to position the marking. This is why the most advanced marking equipment offers many marking parameters and options:
- Straight marking: this is the most common solution which allows you to mark horizontally
- Angular marking: this type of marking offers the possibility of adjusting the marking up to 360° in order to optimize the positioning
- Radiant marking: the marking follows a circular path to follow the outline of a cylinder
- Mirror marking: this solution allows to reverse the reading of the marking on translucent parts such as Plexiglas, so that it is readable once the part is turned over.
- Marking on cylinders: this allows to mark cylindrical surfaces either on its circumference or on its tangent
- Multi-level marking: this option allows marking several surface heights on the same part in one operation




